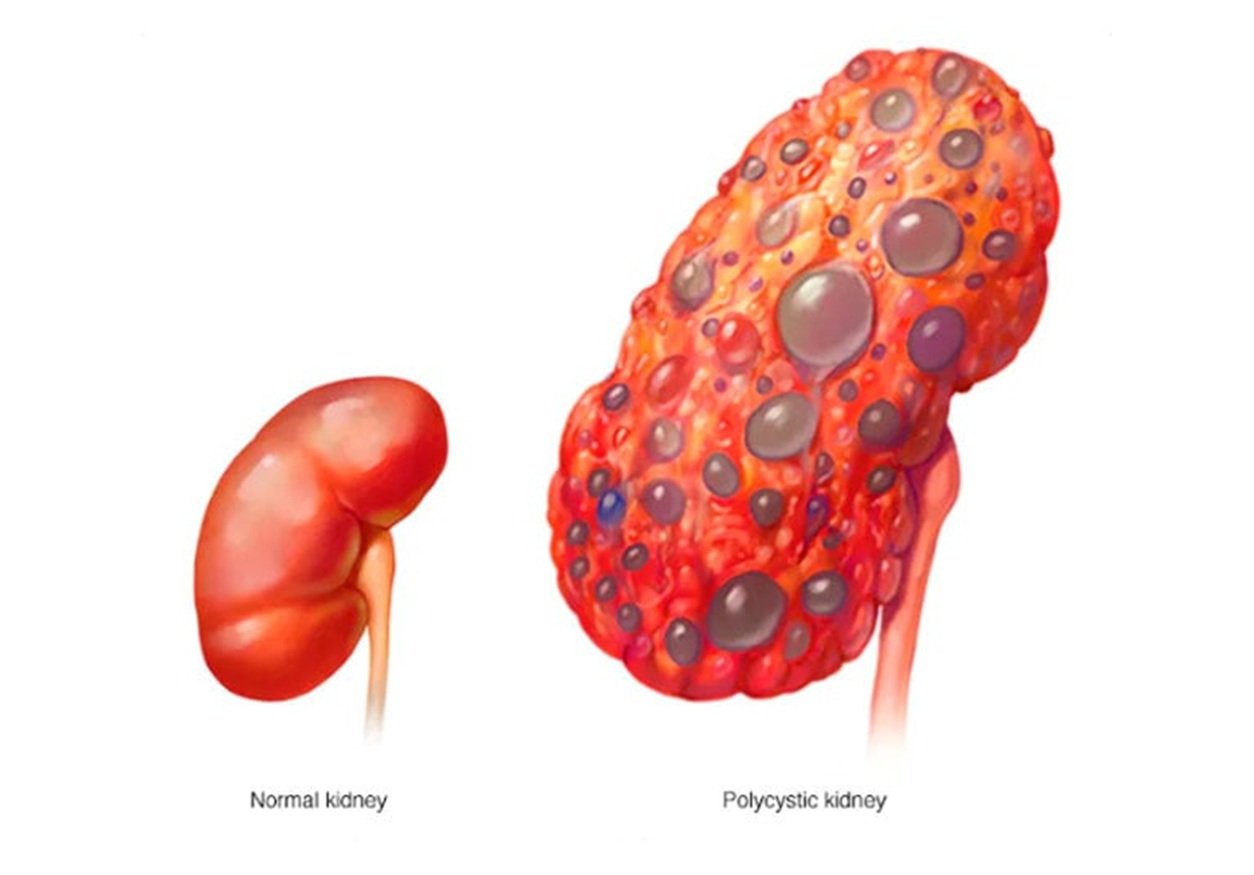
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder that will cause many cysts to form in the kidneys, resulting in kidney enlargement and an eventual loss of function. PKD is a major health issue in the USA, impacting thousands of people. Good management is key to delaying disease progression and improving the quality of life for people with the disease.
What You Need to Know About Polycystic Kidney Disease
There are two main types of PKD:
- Autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD): about 90 percent of cases, usually causes kidney dysfunction in adulthood. It makes up most of the cases of PKD.
- Autosomal Recessive PKD (ARPKD): Less common, ARPKD is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.
Both forms lead to the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys that can damage kidney function over time.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
People with PKD can see symptoms like high blood pressure, abdominal pain, blood in the urine, and frequent urination. Diagnosis typically includes imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to identify kidney cysts. Genetic testing can confirm whether the disease is present.
Management Strategies
There’s currently no cure for PKD, but a number of management strategies can help control symptoms and slow disease progression:
Blood Pressure Control
It is important to keep your blood pressure within the normal range.ACE inhibitors help treat high blood pressure in PKD. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are also commonly used.
Pain Management
PKD often causes abdominal or back pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers may help, but be sure to speak with your healthcare provider before using. Sometimes more advanced interventions are required.
Lifestyle Modifications
Embracing a healthy lifestyle can slow disease progression significantly.
- Diet: A cross-disciplined diet, low in sodium and protein, will help control blood pressure and reduce kidney workload.
- Fluid Intake: Alkaline water or other high-phosphate drinks would also benefit the kidneys.
- Difficulty: Finding time to exercise and to keep a balanced diet.
- Regular health checkups and continuous health monitoring
Blood tests and imaging to check kidney function should be done regularly. If complications are caught early, interventions can be applied in a timely manner.
Advanced Treatments
In late-stage PKD, possible treatments could be:
- Dialysis: Dialysis can serve the kidney’s filtering functions for patients with end-stage kidney failure.
- Kidney Transplantation: Patients who are eligible may undergo kidney transplantation to restore renal function.
Support and Resources
Southern Oklahoma Kidney Center provides access to essential support and resources for those affected by PKD. USA-based charities, such as the PKD Foundation, offer valuable information, emotional support, and practical advice for managing finances.
PCOS management, which includes lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring, plays a crucial role in overall health. Individuals with PKD can continue to live full lives with the right healthcare providers and the tools currently available.